Dee Leopold just announced (30 May 2013) the full application deadlines and key application components on the From the Admissions Director blog. I will post my full analysis of the entire application after its release, but I wanted to provide an immediate reaction to what is a dramatic change:
This is the only "essay" question:
"You're applying to Harvard Business School. We can see your resume, school transcripts, extra-curricular activities, awards, post-MBA career goals, test scores and what your recommenders have to say about you. What else would you like us to know as we consider your candidacy?"
That's it. No word limit. Use your own judgment as to how much to tell us. We have neither a "right answer" nor a "correct length" in mind. We will review all the elements of the written application to decide who moves forward to the interview stage of our process.
HBS is a place for promising people to become better. This year, HBS is asking applicants an open-ended question that reflect this spirit. In past years, HBS has asked questions that simply were more specific and that could prove difficult to answer. This year, any size, fits all!
When no essay is a good idea: I don’t actually recommend going completely essay-less unless you are absolutely certain that you really don’t have anything to add beyond your resume, test scores, application form content, and what you think your recommenders (Reduced from the longstanding three to two recommenders for you!) are likely to write about. If you are a super star and have no time to write an essay, of course, this is a highly viable strategy. For those less certain of their superstardom and the time to write an essay, I would surely recommend doing so.
Just to state the obvious: Don’t be redundant. I think the most important thing is that whatever essay you give HBS it really does need to go above and beyond what they will be able to understand from the rest of your application. In this respect, taking care of your resume and application form content first is really important because you want to fully consider what they will know and be able to easily understand about you without having to read an essay. As far as the recs go, since you don’t have full control over their contents, but only your selection of recommenders, consider what they are likely to say about you. After you have fully considered the objective aspects of what you will provide, then consider what else you need to say.
I’ll incorporate this post’s content into a longer full post on the HBS essay in early June. Below, I discuss possible sources of content for this essay by considering the three primary stated criteria and one overall consideration that HBS uses in selecting candidates because this can form the basis of a successful admissions strategy.
Four Ways HBS Evaluates Applicants
My objective when working with each of my clients is to help them identify the best content in their essays, resume, interview and other application components to show fit for each school they apply to. My approach is to understand the audience that is being communicated to because the only objective of your application is to communicate effectively to your audience, the admissions committee.
The following summarizes what HBS is looking for (Diversity, Habit of Leadership, Analytical Aptitude and Appetite, and Engaged Community Citizenship) and the possible places where you can demonstrate these in your initial application (Interview and post-interview not considered below):
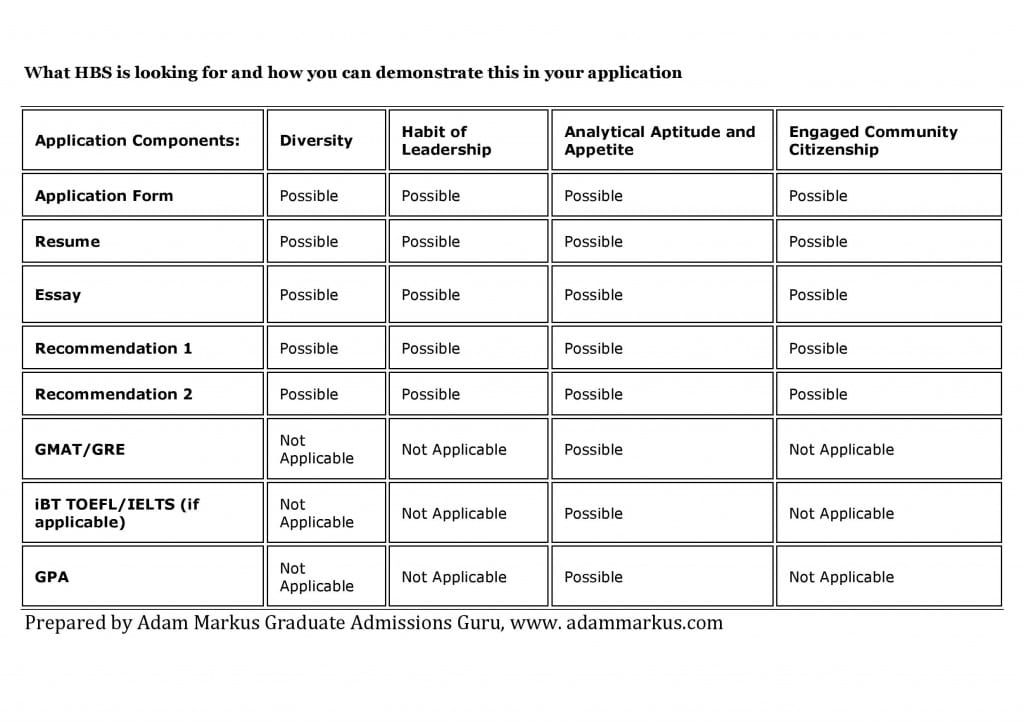
These four core ways that HBS evaluates applicants need to be communicated in your application and one or more of them should be used in your essay. HBS makes their own core selection criteria clear: Please read "Who Are We Looking For?"
Diversity
Instead of looking for an “ideal” candidate, HBS invites applicants who bring a variety of skills, accomplishments, and aspirations to form a very special community. To create a dynamic environment that mirrors the breadth and depth of our world economy, we seek diversity. Our promise to our faculty and to every student here is to create a class of 900 students who come from as many different backgrounds and perspectives as possible.
This overall intention to create a highly diverse class significantly impacts HBS admissions’ decisions. The critical thing is that you demonstrate why you are unique and how you will add to the diversity of the class. In your essay you need to show what makes you stand out. Especially if you think your academic, personal, professional, and/or extracurricular experiences are not inherently unique, it is very important that your essay demonstrates what makes you stand out.
Some ways of demonstrating diversity that my clients have used successfully include the following:
-Being the first person or kind of person to do something
-Being the youngest person to do do something
-Making an original contribution to something
-Having an unusual family, academic, personal, or professional background
-Unusual skills or talents
-Extensive international experience
-Receiving prestigious awards or scholarships
-Even post-MBA goals might be used for this purpose if your goals help to make you stand out.
Keep in mind that diversity is a matter of interpretation and presentation and it is each applicant’s responsibility to best demonstrate how they will add value to their classmates. One of my jobs as a consultant is always help my clients identify ways that make them distinct even if they think they are not special. I operate on the assumption that everyone is unique.
Habit of Leadership
The mission of HBS is to educate leaders. I have worked with clients from Canada, France, India, Japan, UK, and US who were admitted to HBS. They had a diversity of educational, extracurricular, and professional backgrounds, but were united by one thing: In one or more aspects of their lives, they demonstrated this habit of leadership. HBS takes a very broad view of what they are looking for:
We recognize – and welcome – leadership that may be expressed in many forms, from college extracurricular activities to academic or business achievements, from personal accomplishments to community commitments. We appreciate leadership on any scale as well, from organizing a classroom to directing a combat squad, from running an independent business to spearheading initiatives at work. In essence, we are looking for evidence of your potential.
HBS does not explicitly ask you to show your potential for leadership in this essay, but it may very well be something you decide to write about. Leadership is no easy thing. Nor is it always obvious. If you leadership is fully obvious from resume, than perhaps your essay not discuss it, but the worst possible thing is to conceive of leadership as simple formal responsibility or a title because this conveys nothing about the person in that position. While some applicants will have held formal leadership positions, many will not. Formal leadership positions are great to write about if they involve the applicant actually having significant impact, making a difficult decision, being a visionary, showing creativity, or otherwise going beyond their formal responsibility, but the same is true for those showing leadership without having a formal title.
If you are having difficulty really understanding leadership, one great place to read about leadership, and business in general, is Harvard Business School Working Knowledge. Also, if you have not done so, I suggest reading relevant essays in 65 Successful Harvard Business School Application Essays: With Analysis by the Staff of the Harbus, The Harvard Business School Newspaper. Reading these essays should help you to understand the great diversity of topics that are possible and not only in terms of leadership.
Engaged Community Citizenship
While "Engaged Community Citizenship" might take the form of leadership, it is quite distinct:
So much of our MBA experience – including the case method, section life, and student-organized events – requires the active collaboration of the entire HBS community. That’s why we look for students who exhibit the highest ethical standards and respect for others, and can make positive contributions to the MBA Program. The right candidates must be eager to share their experiences, support their colleagues, and teach as well as learn from their peers.
HBS and other MBA programs are looking for students who will make a contribution. This really makes sense because of the collaborative nature of MBA education. While professors play an important role in the classroom, students learn from each other on a continuous basis both inside and outside of class. An MBA education is very much one based on relationship building. One of the chief functions of an MBA admissions committee is to select people who will be good classmates. The director and the rest of the committee have done their job properly if they have selected students who can work well together, learn from each other, and if these students become alumni who value the relationships they initially formed at business school. Given that two of the major takeaways from an HBS education are the relationships that a student forms during the program and access to the alumni network, HBS is looking for candidates who will fully engage with others.
The essay question that HBS asks does not require one to directly discuss contributions. Actually in most HBS essay sets in the past, community engagement is not directly requested. I would argue, in fact, that even if a school does not ask an applicant to tell them what he or she can contribute, the applicant should make that clear in the essay(s) by showing the ways one has added value to others, teams, organizations, projects, etc. Interviews are usually a further opportunity to discuss how one will make a contribution. It is important to show engagement with others in your HBS essay, in your interview, in your post-interview essay, in your application, and in your resume. You should also make it a point to get your recommenders to discuss how you add value to the team, to whatever "community" (A workplace is a community) they worked with you in.
Engagement in a community may take many different forms. Over the years, I have found the following types of activities to be very effective for MBA applications:
-Volunteer or social activities at work, whether it is actually organizing them or participating in them.
-Volunteer or social activities at school, whether it is actually organizing them or participating in them.
-Volunteer or social activities outside of work or school, whether it is actually organizing them or participating in them.
-A volunteer activity related to your post-MBA goals
-A volunteer activity that allowed for the development of leadership and/or teamwork experience
-A volunteer activity that put you in contact with people who are quite different from you in terms of nationality, income level, and/or educational background
-An international volunteer or social activity
-Active involvement in an alumni organization
-Active participation in a sports team
-Active political involvement (Not just voting or knowledge of politics, but actual activities)
-Participation in an orchestra, band or other musical group
-Participation in drama or dance
-Organizing trips or other activities for a group of friends
-Serving as the leader, organizer, or active member of a team-based educational activity such as a seminar, project, or overseas trip
The above are just some possibilities.
Some people will no doubt worry that they lack extracurricular activities to demonstrate such community citizenship, but in my experience there is always some way to demonstrate this. Part of my job is to help my clients identify such activities and communicate about them effectively. If you have demonstrated extensive community citizenship in your resume, you may very well not to write about in the HBS essay this year, but you might still find that explaining your motivation for such activities is something you want to convey to HBS. For those with limited objective resume content in this area, if there is an effective way to get some positive aspect of your community citizenship into the essay, do so.
Analytical Aptitude and Appetite
Harvard Business School is a demanding, fast-paced, and highly-verbal environment. We look for individuals who enjoy lively discussion and debate. Our case and field-based methods of learning depend upon the active participation of prepared students who can assess, analyze, and act upon complex information within often-ambiguous contexts. The MBA Admissions Board will review your prior academic performance, the results of the GMAT or GRE, and, if applicable, TOEFL iBT and/or IELTS, and the nature of your work experience. There is no particular previous course of study required to apply; you must, however, demonstrate the ability to master analytical and quantitative concepts.
HBS is a highly competitive and challenging academic environment. It is not for anyone. "Analytical Aptitude And Appetite," what can more generally be thought of as academic potential, will be very easy for some candidates to demonstrate without ever writing an essay on the topic. You must demonstrate your analytical intelligence somewhere in your application. Yes, a solid GPA and GMAT are enough for that purpose, but if you think your academic record and GMAT are weak, I do suggest demonstrating your high analytical aptitude and appetite in your essay. Also, whether you address your analytical abilities in your essay, for most applicants, it would also be very useful to have one or more recommenders discussing this.
Some effective ways to demonstrate analytical intelligence include the following:
-Solving a complex problem at work, school, or elsewhere
-Discussing the successful completion of complex analytical tasks
-Breaking down a complex problem that you solved and communicating it a very brief and clear way
- Demonstrating great personal insight into ones weaknesses, failures, and/or mistakes
-Showing the ability to learn from weaknesses, failures, and/or mistakes
-Showing the ability to learn and master something highly complex
-Demonstrating a high level of creativity
Those with truly outstanding academic background and test scores need to likely focus less attention on this area. If you think you have weaknesses in this area, consider how to use the essay to mitigate them.
In my full analysis that I’ll prepare in early June, I’ll discuss more about possible ways to structure the essay, some key ways of telling stories, and how to discuss goals. Since the essay topic is so completely open-ended my objective will be suggest some possible options, but this is clearly a topic where each applicant should really consider what way(s) to best represent themselves.
Here are a few things to remember when you start writing:
Your reader must understand you. Provide a clear interpretation of what you have done. Write in simple language, even about complex things. Assume your reader has a basic business background, but don’t assume any expertise. Cause-effect relationships should not be merely implied where possible. Showing your actual action steps is critical. A full explanation might be impossible because of word count, but if you tell things in sequence, it usually provides that explanation.
You reader must believe you. If your reader is not convinced by your story, you are dead. I am all in favor of telling the best version of a story that you can, provided it is also believable. Bad self-marketing is frequently based on lies that can be seen through. I have met many admissions officers and while not all of them were brilliant, all the good ones had finely tuned “bullshit detectors.” If your essays have a seemingly tenuous relationship with reality, you are likely to be setting yourself up for a ding.
Your reader must be engaged. If a reader does not become interested in what they reading, there is a problem. The problem may be that the essay is simply generic or it might be the way a story is being told is boring or it maybe a lack of passion in the writing. Whatever the case, it needs fixing. One of my roles as a consultant is to coach my clients on writing essays that will be engaging.
You must sell your reader on your high potential for admission. Great essays don't just need to be believable and interesting, they have to be convincing. You are trying to get HBS admissions to take a specific action after they read your file: invite you for an interview. Thus, essays must convince them to take action, they have to see why you should be admitted. I help my clients understand how to do this and give very specific advice on how to do so.
Your reader should be interpreting your essay the way you intend. In writing there is always room for misinterpretation. If you have not effectively interpreted yourself, there is always the possibility that your reader will draw opposite conclusions from what you intended. I help my clients make sure that they understand and correct for all such negative interpretations.
And finally…
My final point is that HBS is looking for people who want to be leaders, not mere managers. They are looking for people who will use their “one precious and wild life” to achieve great things, not those who will be satisfied at being mediocrities. If you can’t show the potential for that now, when will you?
If you are seeking one-to-one advising, I provide that to select applicants every year. My comprehensive service clients have been admitted to the regular HBS MBA for the Classes of 2015, 2014, 2013, 2011, 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007, and 2005 and one 2+2 client admitted to the Class of 2014. My clients’ results and testimonials can be found here. In addition to providing comprehensive application counselling on HBS, I regularly help additional candidates with HBS interview preparation. I have worked with a large number of applicants from Canada, Europe, India, Japan, other parts of Asia, and the United States on HBS application. I think that this range of experience has helped me understand the many possible ways of making an effective application to HBS.
-Adam Markus
I am a graduate admissions consultant who works with clients worldwide. If you would like to arrange an initial consultation, please complete my intake form. Please don't email me any essays, other admissions consultant's intake forms, your life story, or any long email asking for a written profile assessment. The only profiles I assess are those with people who I offer initial consultations to. Please note that initial consultations are not offered when I have reached full capacity or when I determine that I am not a good fit with an applicant.